― Stakeholder Engagement ―
|
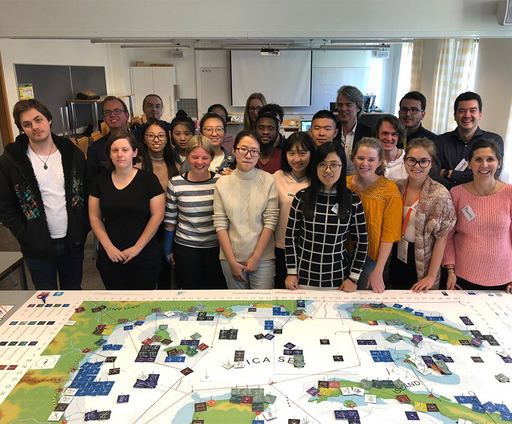
Maritime Spatial Planning is stakeholder oriented. Often across National borders. Engaging and committing stakeholders to a planning process can be a real challenge. The MSP Challenge literally puts stakeholders around the table and facilitates their dialogue.
Use: The MSP Challenge has been used extensively to encourage the involvement of stakeholders. For transboundary stakeholder sessions in ecology, shipping and energy in the Baltic Sea, the North Sea and Clyde Marine area. To support the implementation of the Scottish National Marine Plan and participation in the development of Regional Marine Plans. In Belgium, to kick start the marine spatial plan revision process. |
|
― Learning & Education ―
|
It is important to educate the next generation of Maritime Spatial Planners. To built a global community of future decision makers, ready to work with smart technologies. The MSP Challenge has been designed to engage. The learning process in the MSP Challenge is highly interactive and 'unfolds' like in a computer game. Step by step, the users discover the rich geo, marine data and sectoral information. They come to understand how the maritime economy influences the marine environment, and experience the strategic behaviour of decision-makers and stakeholders.
Use: Nearly a thousand students and young professionals from various parts of the world have experienced the MSP Challenge as an interactive learning environment. Copies of the board game are available at many educational institutions and faculties such as environmental sciences, urban planning, and ocean governance. The simulation game has been adopted as a recurring learning event - such as summer schools - by universities around the world. From Delft, Oldenburg to Venice. From Canada, Finland, to the Maldives and China. |
|
Learning Concepts:
|
Learning Objectives:
|
― Planning ―
|
Planning is co-design, jointly developing concepts and plans for the future. This requires design iterations. Interactive digital tools can support things like ideation, sketching, consultation, evaluation and revision. Making it possible for anybody to contribute. The MSP Challenge simulation platform is a most advanced platform to support this form of planning.
Use: Since its launch in 2018, the MSP Challenge simulation platform has been used for transboundary stakeholder sessions in ecology, shipping and energy in the Baltic Sea, the North Sea and Clyde Marine area. |
|
|
Planning Concepts:
|
Functionalities:
|
― Research & Development ―
|
Maritime Spatial Planning is evidence-based. Getting access to proper data is only the first challenge. How to integrate a large volume and variety of data that may come in different formats, into one platform, is another. To arrange that, multiple scientific simulations can read the data for evaluation and assessment purposes to give an integrated assessment of the dynamic consequences of planning decisions. The MSP Challenge simulation platform is a most advanced platform for such integrated assessment. A flexible platform for R&D in disciplines such as environmental and marine sciences, data science, planning, or even modelling, simulation and gaming.
Use: The MSP Challenge simulation platform works closely together with Ecopath International Initiative. Researchers in different parts of the world have developed foodweb models with Ecopath, and with our help connected it to the MSP Challenge. The MSP challenge features in pending Master and PhD research. Interested to explore how the platform can be used for your R&D? Best send us an email. |
|
Features:
|
Use Cases:
|
― Ecology ―
|
Maritime Spatial Planning is eco-system based. Human activities at sea create pressures, such as noise and bottom disturbance. This impacts the marine environment, through the foodweb. MSP Challenge has a unique link with the foodweb model, Ecopath with Ecosim (EWE). This makes it possible to assess the impact of human activities, such as shipping, energy on the marine environment, over a longer period of time. It also calculates the effect of marine protection measures, such as MPAs and levels of protection for instance against fishing. At the same time, users can decide to reduce fishing efforts in their country.
Use: The MSP Challenge simulation platform works closely together with Ecopath International Initiative (EII). Researchers in different parts of the world have developed foodweb models with Ecopath, and with our help connected it to the MSP Challenge. |
|
― Shipping ―
|
Shipping and fishing are strong pillars of the blue or maritime economy. However, short sea shipping or oceanliners, bulk, container or cruises, do not always have the same interests. How will new emerging sectors in the blue economy such as offshore windfarming affect the various forms of shipping? What is the dynamic impact of shipping on the marine environment? The MSP Challenge simulation platform incorporates plenty of shipping data layers, such as routes and ports, based on satelite data. To assess the consequences of planning decisions, an integrated shipping simulator dynamically generates new shipping routes, tonnages and port efficiencies. |
― Energy ―
|
The transition towards sustainable energy production is one of the most significant drivers behind Maritime Spatial Planning. Many oil and gass riggs will be decommissioned. At the same. offshore wind farming is rapidly stepping up, to create tensions with other sectors, such as shippers and fishers. And there are innovations in technology production, such as wave and tidal energy. Perhaps different energy and conservation functions can be combined. Countries can jointly develop energy infrastructure and share energy production. The MSP challenge is a most advanced platform to guide a search for marine space. Ecology, shipping and energy simulators interact smartly for an integated assessment of the ecological and economic consequences of off shore wind farm development. |
― Serious Gaming ―
|
A simulation game or serious game is an excellent communication and learning tool for planning, decision-making, learning and education. Through game-play, planners and stakeholders experientially understand the dynamic interrelations among various subsystems, the interdependencies among the actors and the consequences of actions well into the future. Game thinking and game technology is at the heart of the MSP Challenge. We take game-based learning to the next level. Because we aim for deep impact in a global community of professionals and experts. Because, we work with state of the art game technology, including AI, VR. And we fuse engagement into digital worlds full of complexity and realism. |
|
|
Game Mechanics:
|
Use Cases:
|